Clostridium Butyricum

About Clostridium butyricum
Clostridium butyricum is a strictly anaerobic spore-forming butyric acid producing bacillus, it has been
widely used as a probiotic in Asia (particularly in Japan, Korea, and China) for both the treatment and
the prophylaxis of human gastrointestinal disease. It also has been demonstrated have positive effect
on improve livestock production performance, prevention of diarrhea, and effectively prevent and
treatment of animal necrotic enteritis.
When orally administered, spores of Clostridium butyricum protect them from being killed by gastric
acids, digestive enzymes or bile, and then germinated in the upper small intestine, Vegetative growth
began in the distal small intestine, and mainly grew and exert positive effect in the distal small intestine,
cecum and colon.
Mode of action
lSCFAs constitute an important energy source for intestinal cells, and have proliferative effects on
enterocytes, maintain the integrity of the intestinal tissue.
lSCFAs have been noted to have immune-modulatory effects on colonic inflammation.
lLower intestinal pH controlling the overgrowth of pathogens and promote the proliferation of
benefit bacteria.
Secret Bacteriocins such as butyricin, inhibited the growth of Clostridium perfringens and Salmonella,
decrease the incidence of necrotic enteritis and other enteric disease.
Prevents colonization of pathogens in the intestine by Competitive exclusion.
Produce hydrogen in the intestine and has a strong repairing effect on various internal organs, especially
liver and spleen oxidative damage.
Effects of GBW Clostridium butyricum on weaned piglets performance
Weaning imposes tremendous stress on piglets, the period following weaning is characterized by a high
incidence of intestinal disturbances with diarrhea and depression of growth performance in piglets.
A filed experiment was conducted to investigate the effects of GBW Clostridium butyricum on growth
and health performance of weaned piglets.
Trail design and results:
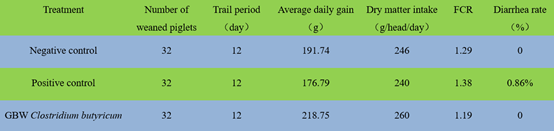
Note:Positive control: 300 ppm Chlortetracycline;
Negative control: no probiotics and antibiotics supplementation;
GBW Clostridium butyricum: 108 CFU/kg compound feed.
Effects of GBW Clostridium butyricum on finishing pigs performance
Supplemented with GBW Clostridium butyricum reduces FCR and increases daily weight gain of
finishing pigs.
Trail design and results:
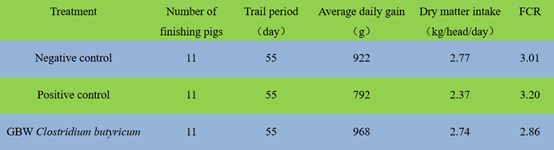
Note:Positive control: 300 ppm Chlortetracycline;
Negative control: no probiotics and antibiotics supplementation;
GBW Clostridium butyricum: 108 CFU/kg compound feed.
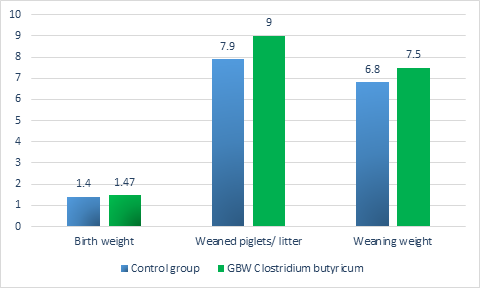
Effects of Clostridium butyricum on performance of Sows and Piglets
Sows and Piglets are the fundamental and future of pig farm respectively, the performance of Sows and
Piglets is critical for a profitable pig production.
Trail design and results:
A total of 22 pregnant sows were divided into two groups. The diet of Clostridium butyricum group
was additional supplemented with 200g Clostridium butyricum per ton compound feed, experiment
start from 10 days pre-partum to the wean of piglets.
Effects of GBW Clostridium butyricum on Jejunum morphology and intestinal
inflammation of LPS challenged broiler
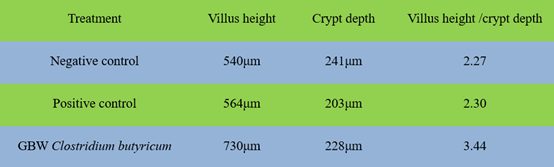
Lengthening of villi increase total luminal villus absorptive area and subsequently result in satisfactory digestive
enzyme action and higher transport of nutrients at the villus surface. Moreover, the higher villus height to crypt
depth ratio in the broilers supplement with GBW Clostridium butyricum resulted in a decreased turnover of the
intestinal mucosa. A slower turnover rate of the intestinal epithelium results in a lower maintenance requirement,
which can finally lead to a higher growth rate or growth efficiency of the animal.
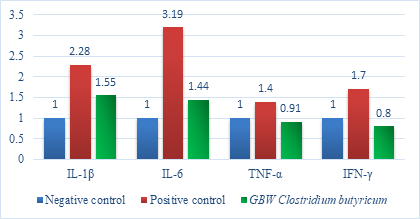
LPS is the main toxin factor of E. coli and salmonella, which cause livestock enteric disease. The results
shows that administrate Clostridium butyricum to LPS challenged broiler can down-regulate the mRNA
expression of Pro-inflammatory factor, mitigate intestinal inflammation.
Note:Positive control: LPS challenge;
Negative control: no probiotics and LPS challenge;
GBW Clostridium butyricum: 108 CFU/kg compound feed.

